One of the most common pathologies of the musculoskeletal system is deforming arthrosis of the hip joint. The progressive process affects the hyaline cartilage, destroying bone and connective tissue. One mobile connection and both were affected. Another name for the disease is coxarthrosis, which manifests more often in women after the age of 40.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The disease is not hereditary, but the presence of genetic characteristics of tissues and bones can cause its development and transmission from parents to children. Hip osteoarthritis is considered an age-related problem, which is caused by the aging of the body. There are cases when the process of destroying the hip joints begins in young people.
The main causes of hip arthrosis include pathologies that cause the pathological process:
- tissue injury (femoral neck fracture, contusion);
- intensive physical activity (sports, weight lifting);
- joint infection (arthritis);
- death of the femoral head;
- obesity;
- endocrine diseases such as diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders;
- scoliosis.
The hip joint is destroyed under the influence of various factors. Therefore, people with genetic predisposition, overweight, heart disease are at risk.
Types of diseases
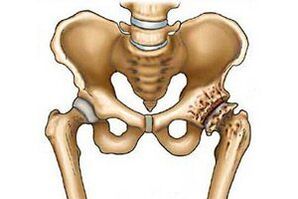
Arthrosis of the hip joint is of two types:
- Primary or idiopathic. It develops after 50 years. It differs in symmetrical joint lesions. The course is disappointing, it is difficult to determine the cause of the destruction of the pelvic joints.
- Secondary. It is characteristic of young age, the stimulus is various pathologies. Defeat of one joint: left or right is characteristic. The course is slow, and if you take the drugs prescribed by the doctor and follow the recommendations, then the pathology responds well to treatment.
The disease leads to complete destruction of the joint.
Degree of coxarthrosis and characteristic symptoms
The process of destroying the hip joint takes place gradually, each of the 3 stages is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- Initial phase. Arthrosis of the 1st degree of the hip joint is accompanied by signs:
- occasional pain in the hip caused by exercise, stress in the pelvis;
- groin discomfort;
- lack of movement restrictions;
- slight narrowing of the joint space.

- 2nd degree disease. Exacerbation occurs, in the pelvic area, the local temperature rises. Pain at rest and during exertion. The development of the 2nd degree of arthrosis of the hip joint is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the pain syndrome is intrusive and intense, especially at night;
- characteristic "initial" pain that accompanies movement after rest;
- restriction of movement, which leads to the destruction of cartilage and inflammation;
- appearance of lameness;
- difficulty in abducting the foot, bending the limbs;
- muscle atrophy, in which the affected leg appears limp;
- the joint space is narrowed, bone compaction occurs during radiography.
- The last one, stage 3. It talks about irreversible processes. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- the joint hurts constantly, the general condition worsens;
- changes in the size of the lower limbs;
- lameness when walking;
- complete immobility of the joint, it blocks the pelvic joint;
- lack of cartilage layer, bone surfaces are connected.
Diagnosis of arthrosis
The appearance of early symptoms does not force a person to go to the clinic, and prefers self-treatment. However, arthrosis of the hip joint requires urgent medical assistance and timely diagnosis. At the consultation, the presence of arthritis, which leads to complications in the form of coxarthrosis, is denied or confirmed. To do this, contact such experts as:
- therapist;
- neurologist;
- rheumatologist;
- orthopedist (surgeon).
The examination is complex, therefore all diagnostic measures are carried out in two directions:
- Clinical diagnostics:
- examination (discovering where it hurts);
- flexion, straightening, rotation of limbs;
- leg asymmetry;
- pain on palpation.
- instrumental review:
- radiography:
- CT;
- MRI;
- ultrasound;
- puncture of fluid from the joint cavity (if necessary).
What treatment is needed?

The goal of all therapeutic procedures is to reduce pain and improve joint mobility. Depending on the degree of damage, the treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint is carried out using several methods.
In the early stage of development, conservative treatment is used, in stage 2 the development of the pathology is stopped, and stage 3 arthrosis can be cured by radical methods.
After confirming the diagnosis of arthrosis of the hip joint, the doctor prepares a series of therapeutic measures consisting of drug treatment and physiotherapy procedures. Treatment is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of pain and inflammation, stopping the process. In more severe cases, surgical treatment with prosthetics is used.
conservative methods
With coxarthrosis of the 1st and 2nd degree of the hip joint, an integrated approach can help: drugs, therapeutic massage, gymnastics, osteopathy. Treating arthrosis non-surgically means preventing surgical intervention. First of all, the doctor prescribes painkillers to alleviate the pain symptoms that constantly accompany arthrosis of the hip joint of the 2nd degree.
Medicines
Drug treatment consists of the use of drugs shown in the table:
| Group | Therapeutic effect |
|---|---|
| Anti-inflammatory (non-steroidal) | Symptomatic, helps to anesthetize the limbs and has an anti-inflammatory effect |
| Steroid hormones | They are used in case there are no results when non-steroidal drugs are used, they help relieve pain and inflammation. |
| Chondroprotectors | Restores the structure of the cartilage tissue, improves the production of synovial fluid |
| Hyaluronic acid | It is injected into the joint to lubricate the joint surfaces |
| Muscle relaxants | Reduce muscle tone, improve blood flow through blood vessels |
Physiotherapy

Massage, exercise therapy, electrophoresis, cryotherapy and many others are useful for coxarthrosis. Let's take a closer look at the main ones:
- Exercise therapy is the basis of therapy. It will help to localize the disease in any part of the body. A special system of exercises will strengthen muscles, remove unpleasant feelings during exercise.
- Massage and manual therapy - passive muscle recovery. It is especially useful in the first stage of pathology development.
- Phonophoresis enhances the action of drugs with ultrasound. If you smear the TBS area with medicine and apply ultrasound, it will quickly penetrate the skin.
- Joint traction. The use of a special device will increase the intra-articular gap.
- Diet. It helps reduce pressure on the joint. Properly selected products improve well-being, but dietary nutrition is not included in the main therapeutic method.
Folk remedies

At home, traditional medicine methods come to the rescue. The patient can be warmed up and put on compresses that relieve inflammation and swelling.
Using compresses with honey, aloe juice, sea salt ensures the rush of blood to the inflamed area, helps to improve blood circulation in it. Folk remedies are part of the complex treatment of initial, as well as 2-3 stages of pathology.
Severe damage is treated with surgery. The diseased joint is replaced with a metal one.
Prevention of arthrosis of the hip joint
It is not difficult to prevent arthrosis of the hip joint. You must adhere to the following recommendations:
- exclude a sedentary lifestyle;
- play sports;
- monitor body weight;
- refuse bad habits;
- timely correct congenital and acquired hip defects.
Coxarthrosis is dangerous, so prevention after 40 years is important for absolutely everyone. But there is also a risk group, which includes athletes and people with a genetic predisposition. When similar symptoms appear, it is important to consult a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis will allow you to receive effective treatment and avoid surgery.





































